This post helps us to learn “Angular 2 Pipes in Depth”
and we will cover most of all questions and answers related to the pipes.
What
is Pipes?
“Pipes transform displayed values within a
template.”
Sometimes, the data is not displays in the well format
on the template that time where using pipes.
You also can execute a function in the template
to get its returned value.
The angular 2 have some additional pipes names
that are async, decimal, percept and so on. And also some of pipes not supported
in angular 2 that are number, orderBy and filter and these are archiving using “custom
pipes”.
Key
Points:-
Pipe class implements the “PipeTransform” interfaces
transform method that accepts an input value and returns the transformed result.
There will be one additional argument to the
transform method for each parameter passed to the pipe.
The “@Pipe” decorator allows us to define the
pipe name that is globally available for use in any template in the across
application.
For
example as,
import { Pipe, PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'barcode',
pure: false
})
export class BarCodePipe implements
PipeTransform {
transform(value: string, args:
any[]): string {
if (!value) {
return '';
}
return "****-****_" + (value.length > 8 ? (value.length - 8): '')
}
}
Angular
2 Built-in Pipes:-
1.
DatePipe,
2.
UpperCasePipe,
3.
LowerCasePipe,
4.
CurrencyPipe,
5.
PercentPipe,
6.
JsonPipe,
7.
AsyncPipe,
8.
And so on..
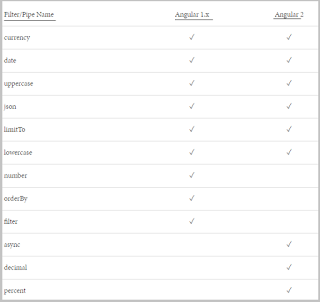
The following table shows a comparison between Angular
1.x and Angular 2.
Why
use Pipes?
Sometimes, the data is not displays in the correct
format on the template that time where using pipes.
You also can execute a function in the template
to get its returned value.
For
example as,
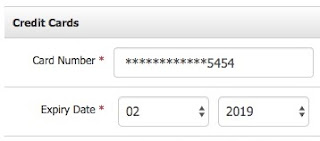
If you want to display the bank card number on
your account detail templates that how to displays this card number? I think you should display the last four digits
and rest of all digits will display as encrypted like (****-****-****_and your card
numbers) that time you will need to create a custom pipe to achieve this.
What
is a pure and impure pipe?
In Angular 2, there are two types of pipes i.e.
1.
pure
2.
impure
The pure pipe is by default. Every pipe has been
pure by default. If you want to make a pipe impure that time you will allow the
setting pure flag to false.
Pure
Pipes:-
Angular executes a pure pipe only when it detects
a pure change to the input value. A pure change can be primitive or non-primitive.
Primitive data are only single values, they have
not special capabilities and the non-primitive data types are used to store the
group of values.
For
example for pipe pure,
import { Pipe, PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'barcode'
})
export class BarCodePipe implements
PipeTransform {
transform(value: string, args:
any[]): string {
if (!value) {
return '';
}
return "****-****_" + (value.length > 8 ? (value.length - 8): '')
}
}
Impure
Pipes:-
Angular executes an impure pipe during every
component change detection cycle. An impure pipe is called often, as often as
every keystroke or mouse-move. If you want to make a pipe impure that time you
will allow the setting pure flag to false.
For
example for pipe impure,
import { Pipe, PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'barcode',
pure: false
})
export class BarCodePipe implements
PipeTransform {
transform(value: string, args:
any[]): string {
if (!value) {
return '';
}
return "****-****_" + (value.length > 8 ? (value.length - 8): '')
}
}
What
is Async Pipe?
Angular 2 provides us special kinds of pipe that
is called Async pipe and the Async pipe subscribes to an Observable or Promise
and returns the latest value it has emitted.
The Async pipe allows us to bind our templates
directly to values that arrive asynchronously manner and this is the great ability
for the promises and observables.
Example
for AsyncPipe with Promise using NgFor,
@Component({
selector: 'app-promise',
template: '<ul> < li * ngFor="let user of users |
async"> Id: {{user.id }}, Name:
{{user.name }} </li>< /ul>'
})
export class PromiseComponent {
//USERS DECLARATIONS.
users = [];
//FETCHING JSON DATA FROM REST APIS
userRestApiUrl: string = 'https://api.github.com/users/hadley/orgs';
//HOME COMPONENT CONSTRUCTOR
constructor(private userService: UserService) { }
//GET USERS SERVICE ON PAGE LOAD.
ngOnInit() {
this.userService.getUsers(this.userRestApiUrl).subscribe(data
=> this.users = data);
}
}
How
to create a custom Pipes?
How
to create a globally available custom “Pipe”?
The “@Pipe” decorator allows us to define the
pipe name that is globally available for use in any template in the across
application.
Steps
for Creating a Custom Pipe:-
1.
Create a typescript class.
2.
Decorate the class using @Pipe.
3.
Implement PipeTransform interface.
4.
Override transform() method.
5.
Configure the class in application
module with @NgModule.
6.
Ready to use our custom pipe anywhere
in application.
In
the below example,
I am using the custom pipe in the user temple to display
our custom “Ids” values at the place of Id.
Table
of Component
1.
user.component.ts
2.
user.service.ts
3.
custom.barcode.pipe.ts
4.
app.module.ts
5.
user.component.html
user.component.ts
:-
import { Component, Injectable} from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { HttpModule, Http } from '@angular/http';
import { UserService } from '../shared/service/user.service';
import { BarCodePipe } from '../shared/pipe/custom.barcode.pipe';
@Component({
selector: 'user',
templateUrl: './user.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./user.component.css']
})
export class UserComponent {
//USERS
DECLARATIONS.
users = [];
//FETCHING JSON
DATA FROM REST APIS
userRestApiUrl: string = 'https://api.github.com/users/hadley/orgs';
//HOME
COMPONENT CONSTRUCTOR
constructor(private
userService: UserService) { }
//GET USERS
SERVICE ON PAGE LOAD.
ngOnInit() {
this.userService.getUsers(this.userRestApiUrl).subscribe(data => this.users = data);
}
}
//END
BEGIN - USERCOMPONENT
user.service.ts
:-
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Http, Response } from '@angular/http';
import 'rxjs/add/operator/map';
//BEGIN-REGION
- USERSERVICE
@Injectable()
export class UserService {
constructor(private _http:
Http) {
}
getUsers(apiUrl) {
return this._http.get(apiUrl).map((data:
Response) => data.json());
}
}
//END BEGIN – USERSERVICE
custom.barcode.pipe.ts
:-
import { Pipe, PipeTransform } from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'barcode',
pure: false
})
export class BarCodePipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: string, args: any[]): string {
if (!value) {
return '';
}
return "....-" + (value.length > 2 ? (value.length - 2) : '')
}
}
app.module.ts
:-
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { UniversalModule } from 'angular2-universal';
import { FormsModule, ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { HttpModule } from '@angular/http';
import { AppComponent } from './components/app/app.component';
import { UserComponent } from './components/user/user.component';
import { HeaderComponent } from './components/shared/header/header.component';
import { MenuComponent } from './components/menu/menu.component';
import { LoginComponent } from './components/login/login.component';
import { RegistrationComponent } from './components/registration/registration.component';
import { UserService } from './components/shared/service/user.service';
import { BarCodePipe } from './components/shared/pipe/custom.barcode.pipe';
import { MyPipePipe } from './components/shared/pipe/test.pipes';
@NgModule({
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ],
declarations: [
AppComponent,
UserComponent,
HeaderComponent,
MenuComponent,
LoginComponent,
RegistrationComponent,
BarCodePipe,
MyPipePipe
],
imports: [
UniversalModule, // MUST BE FIRST IMPORT. THIS AUTOMATICALLY IMPORTS BROWSERMODULE,
HTTPMODULE, AND JSONPMODULE TOO.
RouterModule.forRoot([ //RouterModule.forRoot method in the module imports to configure
the router.
{ path: '', redirectTo: 'user', pathMatch: 'full' },
{ path: 'user/:id', component: UserComponent }, //HERE ID IS A ROUTE PARAMETER.
{ path: 'login', component: LoginComponent },
{ path: 'registration', component:
RegistrationComponent },
{ path: '**', redirectTo: 'user' }
]),
FormsModule,
ReactiveFormsModule
],
providers: [UserService]
})
export class AppModule {
}
user.component.html
:-
<div class="row">
<div class="col-lg-12">
<div class="ibox float-e-margins">
<div class="ibox-title">
<h2>Angular 2
- User Services</h2>
</div>
<hr />
<div class="ibox-content">
<div class="table-responsive">
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name </th>
<th>Description </th>
<th>URls </th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr *ngFor="let user of users; let i =
index" class="tbl-row-border">
<td>{{user.id | barcode: true}}</td>
<td>{{user.login}}</td>
<td>{{user.description}}</td>
<td><a href="{{user.public_members_url}}" target="_blank">{{user.public_members_url}}</a></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Result –
I hope you are enjoying with this post! Please
share with you friends. Thank you!!